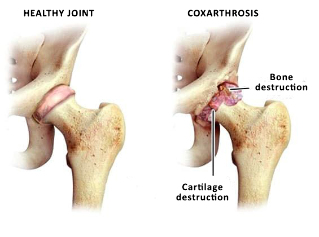
Coxarthrosis - degenerative disease that leads to destruction of the hip joint, and has a chronic course. More common in the older age groups. More common in women than in men.
The onset is gradual and progresses slowly. You can affect a single joint or a combination of both. It is the most common type of osteoarthritis.
Why is it a disease?
Osteoarthritis in some patients, which is accompanied by the natural process of aging is the degeneration of the tissues of the hip joint. Its appearance is influenced by the following factors:
- reduce the tissues of the diets;
- congenital anomaly of the hip joint, in particular dysplasia;
- damage to the pelvic bone;
- post-infectious hip;
- aseptic necrosis of the head of the hip joint;
- Perthes disease (osteochondropathy).
Unfortunately, to determine the cause of the disease is not always possible, and the pathology of the hip joint is called the idiopathic coxarthrosis - it is, therefore, the cause of which has not been established. This is an incentive for the continued study of the problem. The scientific part of this field and the doctors came to the conclusion that an increased risk of osteoporosis observed in these patients:
- The hereditary predisposition to pathology. Patients whose parents had suffered from a disease of the cartilage and the bone, in most cases, you will have these issues.
- The excessive weight gain. The significant weight of the weight of the load on the joints, which are regularly exposed to mechanical parts;
- A metabolic disorder in diabetes mellitus. This leads to a poor supply of oxygen and nutrients into the joint tissues, causing them to lose their properties.
Knowledge of the major risk factors for the disease, and the design of preventive measures in order to prevent this from occurring.
How do you identify the pathology of the hip joint?
The symptoms of osteoarthritis depend upon the anatomical characteristics of the musculoskeletal system, and the reasons for the pathology and the stage of the process. Take into account the main clinical manifestations:
- the painful joints;
- the irradiation of pain in the knee, the thigh and the groin;
- the stiffness of the movement;
- reduced mobility (prm);
- a breach of the walk, round;
- the reduction of the mass of the thigh muscles;
- the shortening of the affected limb.
The clinical picture corresponds to the internal changes in the tissues of the joint. The symptoms increase gradually and in its early stages, the patient is not paying them enough attention. This is dangerous, because it is at the beginning of the healing process, brings about a greater effect.
The clinical and the radiological degree of osteoarthritis of the
The following are the symptoms that are typical of each stage.
- The 1 level. The patient is experience is intermittent pain and discomfort. The discomfort bothers you after a workout, a long position in a static pose. Pain is localized to the area of the joint and course through the rest. At this stage of the proceedings does not affect the walk, and don't shorten your legs. The changes are visible on radiographs - joint space narrowing, there are osteophytes (bony growths).
- The 2 level. To increase the intensity of the pain can occur during rest and radiates to the nearby areas of the body. Appears to be limp under the man-is he or val. A limited range of motion in the joint. In parallel, the change in the x-ray images: the displaced head of the femur, osteophytes grow on the inside and outside edges of the acetabulum.
- Stage 3. The pain becomes constant, it is in the day-and night-time. A lot worse, walking appears as a permanent limp. A drastic decrease in motor function, atrophy of the leg muscles. changing the muscle tissue causes the legs slightly drawn up and become shorter. This can lead to the deformation of the body posture and curvature of your body. The radiograph at this stage of the process: the decrease of the gap between the surfaces of the joint, deformity of the femoral head, is important in the growth of osteophytes.
The diagnostic program, when the disease
The main method of diagnosis - x-ray. It can be used to determine the presence of the disease and its stage. The radiography is to analyse the structure of the joint, on the theme of a narrowing of the joint space, osteophytes, fracture of the head of the hip bone.
If there is a need to take stock of the condition of the soft tissues, an MRI may be obtained. This makes it possible to study in detail the condition of the cartilage areas of the joint, and the muscles of the hip region.
Modern methods and methods of treatment of coxarthrosis of the hip joint
Treatment of osteoarthritis can be conservative and surgical. Treatment of osteoarthritis is aimed at the following objectives:
- the reduction of the pain symptoms;
- the restoration of motor activity;
- rehabilitation and rehabilitation;
- the prevention of complications;
- to improve the quality of life for the patient.
The beginning of the treatment is a change in the risk factors. If you want to do this, the doctor recommends the following actions:
- the normalization of body weight.
- the prevention of harmful habits;
- diet;
- the normalization of physical activity;
- well-balanced drinking regime;
- a healthy sleep.
Conservative treatments include: drugs and the drug-free. Treatment includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics, chondroprotectors. They reduce the inflammation in the tissue, eliminates swelling, and pain, to restore range of motion, and improve the condition of the cartilage.
Non-drug treatment includes, among other things, a massage of the affected area. It stimulates the muscles, which are opposed to their degradation, and the prevention of the shortening of the limb. The comprehensive, professional massage, by stimulating blood flow to the area of the joint, and this, in turn, leads to the normalization of metabolism in the tissues. Please keep in mind that a massage is not always helpful, if a coxarthrosis - it is only during exacerbations and at certain stages of the process. Define your your doctor can recommend the massage techniques, the multiplicity of treatments and the duration of the course.
Obligatory condition of treatment is physiotherapy. It is the prevention of contractures and progression of the disease. The exercises should be done each and every day, it is only then that they will be able to have an effect. The exercises are chosen on an individual basis and it is prescribed by a doctor. Exercises to improve overall health, reduce the risk of an emotional disorder, the strengthening of the powers of the body.
Physical therapy is the other method, which is applied in coxarthrosis. It may be mud, medical baths and showers, magnetotherapy. It uses an electro - and phonophoresis of medicinal substances.
If this method of treatment brought no effect, or have been used to of late - the surgical treatment is needed.
Surgery with coxarthrosis
Surgical treatment is applied with the ineffectiveness of conservative method. This is especially true for the late diagnosis. The modern operational techniques and high quality equipment, that works to enable you to restore the structure and function of the joint, to restore a human's range of motion, and a normal quality of life. The most effective method of surgical treatment is arthroplasty.
The indications for surgery are the following:
- coxarthrosis from 2 to 3 degrees;
- the lack of effect of a therapy;
- the total limit of the movement of walking.
Contra-indications, which do not allow to perform the operation:
- decompensated kidney function, the heart, the liver;
- mental ill-health;
- the acute phase of the inflammatory process in the body.
For this purpose, the preoperative diagnosis. However, if it is possible to adjust the condition of the patient, preparation for surgery and after the surgery.
The operation involves removal of the affected tissue and the prosthesis. There are different models of implants. A variety of methods of attaching the bone – cement and cement free of charge, the material from which the endoprosthesis. For all of the features of the prosthesis and the complexity of the surgery you can get information about consultation with the attending physician.
The recovery period after the surgical treatment
From the first day after surgery, rehabilitation is carried out under the supervision of a medical doctor. For the first time, she had to carry out passive movements, and then the load is gradually increased. Walking in for the first time, it is allowed only with crutches, may be the seat and squat.
Of course, for the first time after the operation, there are restrictions on the loads. Don't be afraid of it because of the performance without the limitations of the keep up to the rest of your life. The reduction of physical activity following the surgical treatment is, there is a need to strengthen the position of the prosthesis, restoration of the integrity of the bone, the healing of the wound. In the 2 months of this, it is necessary to exclude the sports activities physical exercise at the joint, a long walk and some exercise. After complete recovery, the person is returned to a normal life, you can do sports and outdoor activities.
The life span of the prosthesis: the vast majority of the companies indicated that the survival rate of about 90% for an observation period of up to 15 years of age.
































